How to solve Outlook Express 2GB limit problem:
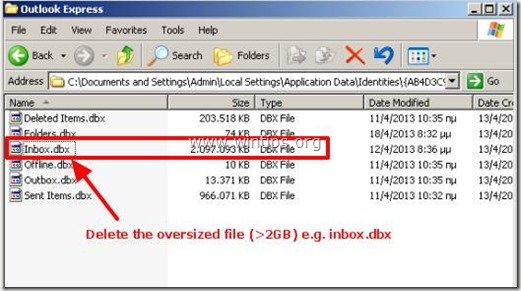
Notice: In this example the symptom is that we cannot receive new e-mails because Inbox.dbx file (Inbox folder) has overridden the 2GB storage limit.
Step 1. Find the Outlook Express store folder.
How to Find the Outlook Express store folder:
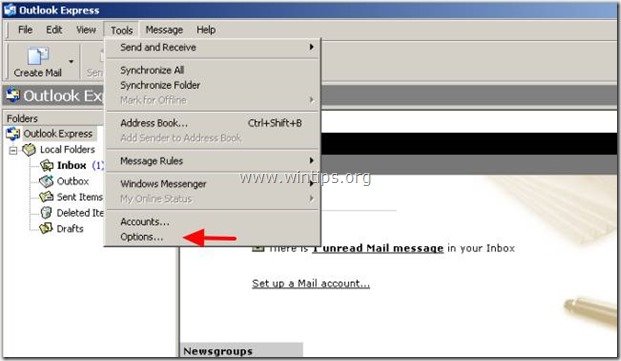
1. From Outlook Express menu, go to: "Tools" > "Options"
2. In Options menu click the "Maintenance" tab.
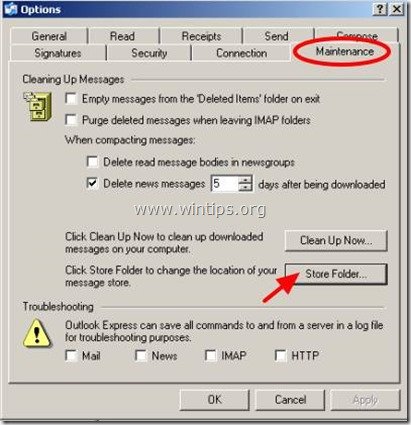
3. In Maintenance tab, click the "Store Folder" button.
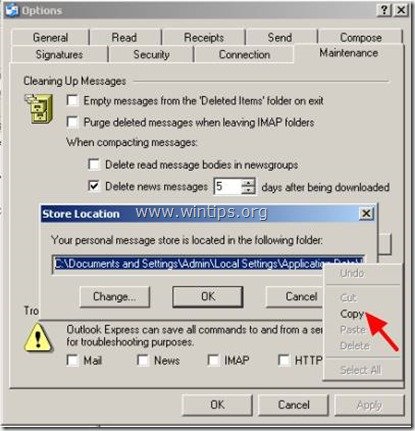
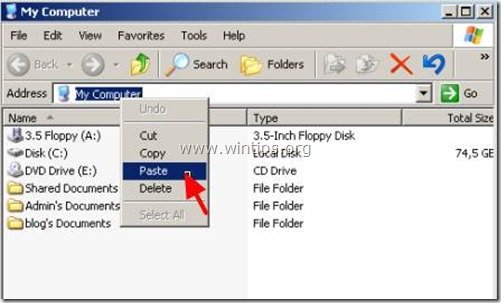
4. Select the entire Outlook Express storage path and then right click on it and select "Copy".
6. Press "Cancel" twice to exit Outlook Express options and then close all Outlook Express windows.
7. Double click to open My computer and in the address bar right click to paste the copied path and then press Enter.
6. From the standard buttons menu toolbar press the "UP" button to go to the parent folder.
Step 2. Take a backup (Copy) of Outlook Express storage folder.
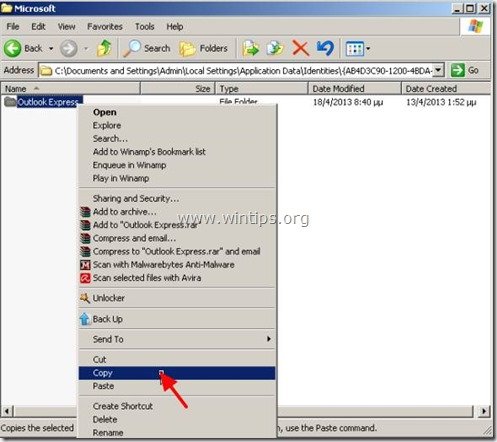
1. Right click on Outlook Express folder and select "Copy".
2. Without closing this explorer window, open an new explorer window and "Paste" the Outlook Express folder in another disk location e.g. in the root folder of drive C:\
Step 3. Delete the oversized Outlook Express file.
1. Open the first explorer window (The location where Outlook Express folder originally stored).
(e.g. C:\Documents and Settings\<your username>\Local Settings\Application Data\Identities\{AB4D….).
2. Double click to open Outlook Express folder.
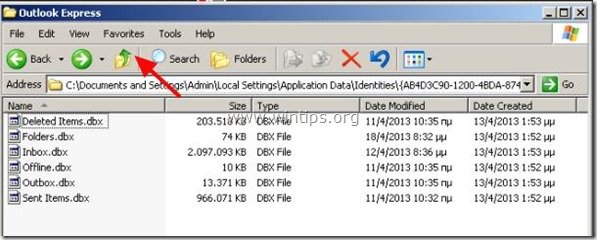
3. Locate and then "Delete" the oversized .dbx file (larger than >2GB, e.g. inbox.dbx, in the above screenshot).
Step 4. Recreate deleted folder (Inbox) folder and then restore (Import) your emails from backup location.
1. Open Outlook Express program.*
Notice:* When Outlook Express opens, recreates the deleted folder (e.g. inbox.dbx) with a new empty folder.
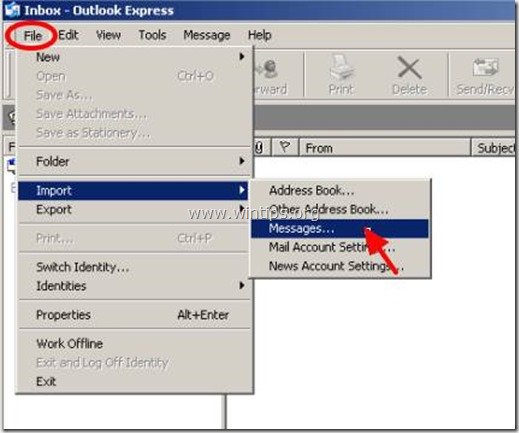
2. From Outlook Express main menu, choose File > Import > Messages.
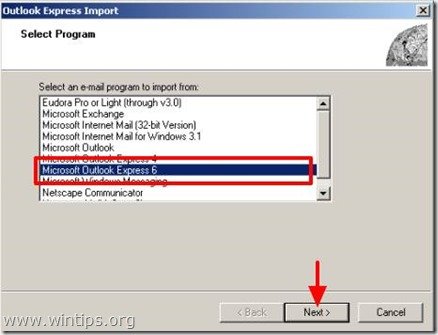
3. In "Select Program" options choose "Microsoft Outlook Express 6" and press "Next".
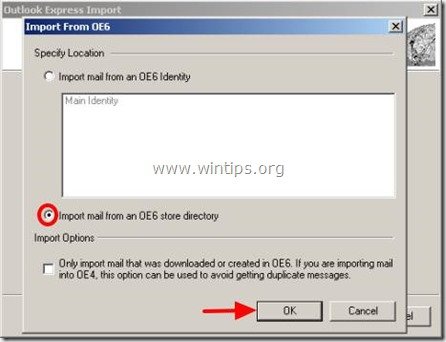
4. In "Specify Location" options, select the "Import mail from an OE6 store directory" option and choose "OK"
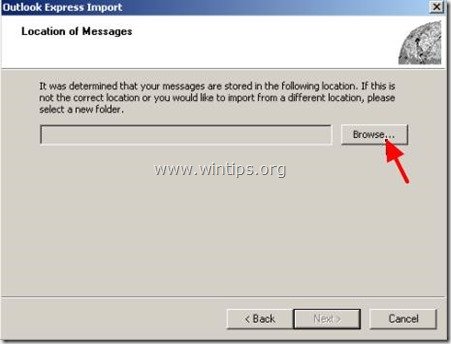
5. In "Location of Messages" window press "Browse" to find and select the Outlook Express backup folder which you had created in step 2. (e.g. C:\Outlook Express)
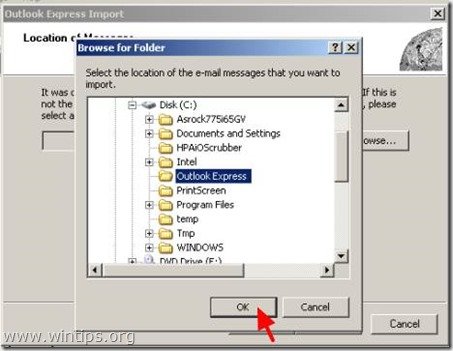
6. Go in the location where you copied (backup) the Outlook Express folder in step 2. (e.g. Disk C:) to select that folder and press "OK"
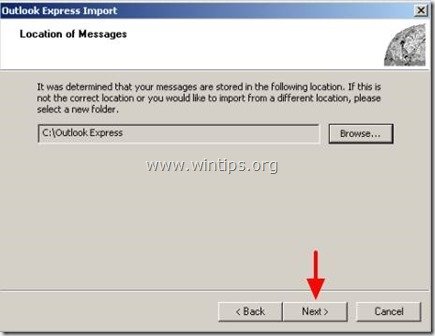
7. After you have selected the Outlook Express backup folder press "Next".
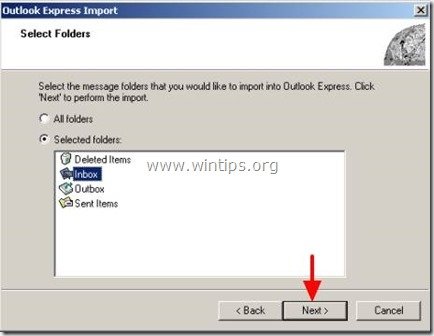
8. Select the Outlook Express folder that you deleted in previous step (e.g. Inbox) and press "Next"
9. Wait until the Import process is completed and then press "Finish".
10. Normally after import operation is completed, you can view all your e-mails again and your Outlook Express program should be working without a problem.
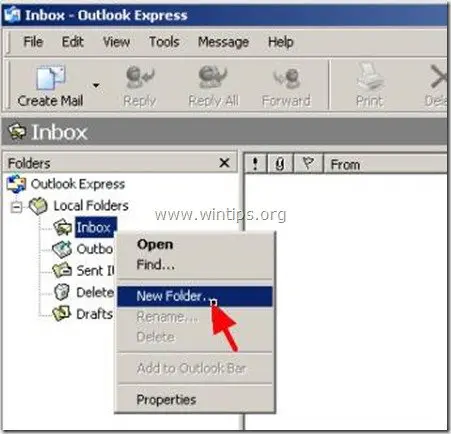
To avoid this problem from happening in the future, the best way is to create different folders inside Outlook Express program and organize/store the mails that you want on it.